Adjusting the color and tone of raw camera files
You can adjust the color and tone of an image by using the following settings.
Color depth
Color depth refers to the number of colors an image can contain. One of the advantages of using raw camera files is that they can contain more colors than photos saved as JPEG or TIFF files. This greater number of colors makes it easier to reproduce colors accurately, reveal detail in shadows, and adjust brightness levels.
The Camera Raw Lab lets you process the raw camera files as 48-bit or 24-bit images. 48-bit images offer more accurate color representation and prevent loss of image quality during retouching. Note that some of the special effects available in CorelDRAW cannot be applied to 48-bit images.
White balance
White balance is the process of removing unnatural color casts from images so that image colors appear as they do in real life. White balance takes into consideration the lighting conditions in which a photo was taken and sets the color balance to produce realistic image colors.
By default, when a raw camera file is brought in to CorelDRAW, it reflects the camera setting for white balance. This setting appears as the preset As shot in the White balance list box. If you are not satisfied with this setting, you can have the white balance adjusted automatically by choosing the preset Auto. You can also apply any of the following presets: Daylight, Cloudy, Shade, Tungsten, Fluorescent, or Flash. These presets let you simulate different lighting conditions.
Raw camera image with incorrect white balance (left); the same image with adjusted white balance (right)
In addition, you can use the Eyedropper tool to automatically adjust the contrast in an image according to the white or gray point that you sample in the preview window.
If the White balance options do not produce the results you want, you can use the following controls to remove color casts:
|
•
|
|
Temperature slider — lets you correct color casts by adjusting the color temperature of an image to compensate for the lighting conditions at the time the photo was taken. For example, to correct a yellow color cast caused by taking a photo indoors in dim incandescent lighting, you can move the slider to the left. Conversely, to correct a blue color cast caused by intense lighting conditions, you can move the slider to the right.
|
|
•
|
|
Tint slider — lets you correct color casts by adjusting the green or magenta in an image. You can add green by moving the slider to the right; you can add magenta by moving the slider to the left. Moving the Tint slider after using the Temperature slider lets you fine-tune an image.
|
Tonal adjustments
You can use the following controls to adjust the tone of raw camera files.
|
•
|
|
Saturation slider — lets you adjust the vividness of colors. For example, by moving the slider to the right, you can increase the vividness of a blue sky in an image. By moving the slider to the left, you can reduce the vividness of colors.
|
|
•
|
|
Exposure slider — lets you compensate for the lighting conditions at the time the photo was taken. Exposure is the amount of light allowed to fall on the image sensor of a digital camera. High exposure values result in areas that are completely white (no detail); low values result in increased shadows. Exposure values (EV) range from -3.0 to + 3.0.
|
|
•
|
|
Brightness slider — lets you brighten or darken an entire image. If you want to darken only the darkest areas of an image, you must use the Shadow slider.
|
|
•
|
|
Shadow slider — lets you adjust the brightness in the darkest areas of an image without affecting the lighter areas. For example, a bright light behind a photo subject (backlighting) at the time a photo is taken can cause the subject to appear in shadow. You can correct the photo by moving the Shadow slider to the right to lighten dark areas and reveal more detail.
|
Using the histogram
While you are making adjustments, you can view the tonal range of the image on the histogram to check for any clipping of shadow or highlight areas. Clipping is the shifting of image pixels to white (highlight clipping) or black (shadow clipping). Clipped highlight areas appear completely white and contain no detail; clipped shadow areas appear completely black and contain no detail.
The button on the left side of the histogram displays a warning if the image contains shadow clipping. The button on the right side of the histogram displays a warning if the image contains highlight clipping. You can also choose to apply shading to the clipped areas in the preview window.
To adjust the color and tone of a raw camera file
|  |
|
1.
|
|
Click File  Import. Import. |
|
2.
|
|
Select the raw camera file or files that you want to import, and click Import.
|
|
3.
|
|
From the Color depth list box, choose one of the following options:
|
| |
•
| |
48-bit (16 bits/channel)
|
| |
•
| |
24-bit (8 bits/channel)
|
|
4.
|
|
To remove a color cast, select the Auto option from the White balance list box.
|
| |
If you are not satisfied with the results, you can set the white point more precisely by using the Eyedropper tool  to sample a white or gray color in your image. |
|
5.
|
|
Perform one or more tasks from the following table.
|
|
To
|
Do the following
|
|
Simulate different lighting conditions
|
Select an option from the White balance list box.
|
|
Correct color in the image
|
Adjust the Temperature slider, and then fine-tune the color correction by adjusting the Tint slider.
|
|
Make colors more vivid or less vivid
|
Move the Saturation slider to the right to increase the amount of color in the image or to the left to decrease the amount of color in the image.
|
|
Adjust exposure
|
Move the Exposure slider to the left to compensate for high-exposure camera settings or to the right to compensate for low-exposure camera settings.
|
|
Brighten or darken an image
|
Move the Brightness slider to the right to lighten the image or to the left to darken the image.
|
|
Adjust the brightness in the darker areas of an image without changing the lighter areas
|
Move the Shadow slider.
|
|
Show clipped shadow areas
|
Click the button to the left of the histogram.
|
|
Show clipped highlight areas
|
Click the button to the right of the histogram.
|
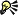
|
•
|
|
You can capture the current version of your image by clicking Create snapshot. Thumbnails of the snapshots appear in a window below your image. Each snapshot is numbered sequentially and can be deleted by clicking the close button in the upper right corner of the snapshot title bar.
|
|
•
|
|
To change a color or tone setting one increment at a time, you can click in the box to the right of a slider, and press the Up or Down arrow keys.
|
|
•
|
|
You can undo or redo the last correction you made by clicking Undo or Redo. To undo all corrections, click Reset to original.
|
Adjusting the color and tone of raw camera files

![]()